Screen printing:
Great for large runs, solid colors, and ultra-durable prints.
Digital printing:
Best for small batches, full-color designs, fast turnaround, and eco-friendly production.

In 2025, textile manufacturers are steadily shifting toward digital printing to achieve greater production flexibility, faster delivery, and more sustainable manufacturing. This article provides a comprehensive comparison between screen printing and digital printing, using the Hanin(HPRT) DA066M Hybrid Digital Textile Printer as a case study to demonstrate how modern production lines can seamlessly integrate screen + digital technologies—enabling a smooth transformation from traditional to fully digital workflows.
What Is Screen Printing and How It Works
Screen printing, also known as silk screen printing, is a classic fabric printing technique that relies on a fine mesh stencil (screen) to transfer ink onto a surface. Each color in the design requires a separate screen, which makes the process ideal for large production runs of the same pattern but less practical for short or customized orders.
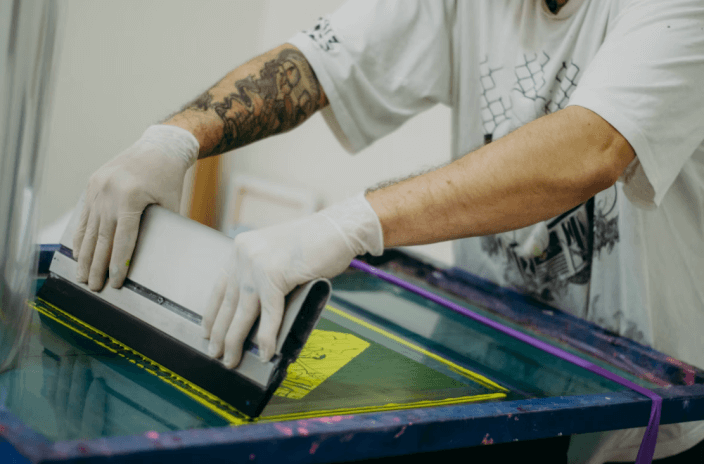

1. Screen Preparation: A stencil of the design is created on the mesh using a light-sensitive emulsion. Each color in the artwork requires its own screen, so multicolor jobs involve several layers of preparation (coating, exposure, developing, and drying).
2. Printing Process: Once the screens are ready, the fabric—such as a cotton T-shirt—is placed on the platen. Ink is poured over the screen and pushed through the open stencil areas with a squeegee. Color layers are printed in sequence to build the final image.
3. Curing and Finishing: The garment is heat-cured to set the ink into the fibers, delivering vivid, opaque colors with a tactile texture and excellent wash durability.
What Is Digital Printing and How It Works (DTG)
What Is Digital Printing
Digital printing directly transfers digital designs onto materials via inkjet systems—no plates or screens required. It offers rapid setup, precise color control, and high-definition results.
In the textile printing industry, digitalization is driving a transformation toward Digital Textile Printing (DTP) — encompassing Direct-to-Garment (DTG), Direct-to-Fabric (DTF), and Dye Sublimation technologies.
Among these, DTG is renowned for its eco-friendly, efficient, and highly flexible process, capable of printing vibrant, detailed designs directly onto cotton T-shirts, canvas bags, and other fabrics — making it the ideal choice for small-batch and customized production.
For manufacturers seeking higher throughput and multi-process capability, the Hanin DA066M Hybrid Digital Textile Printer combines DTG flexibility with industrial-grade productivity, delivering a fully integrated digital solution that supports the entire workflow—from creative sampling to large-scale production.
Interested in sublimation printing? Read Insights from Dye-Sublimation Printer Manufacturer: Sublimation vs Screen Printing
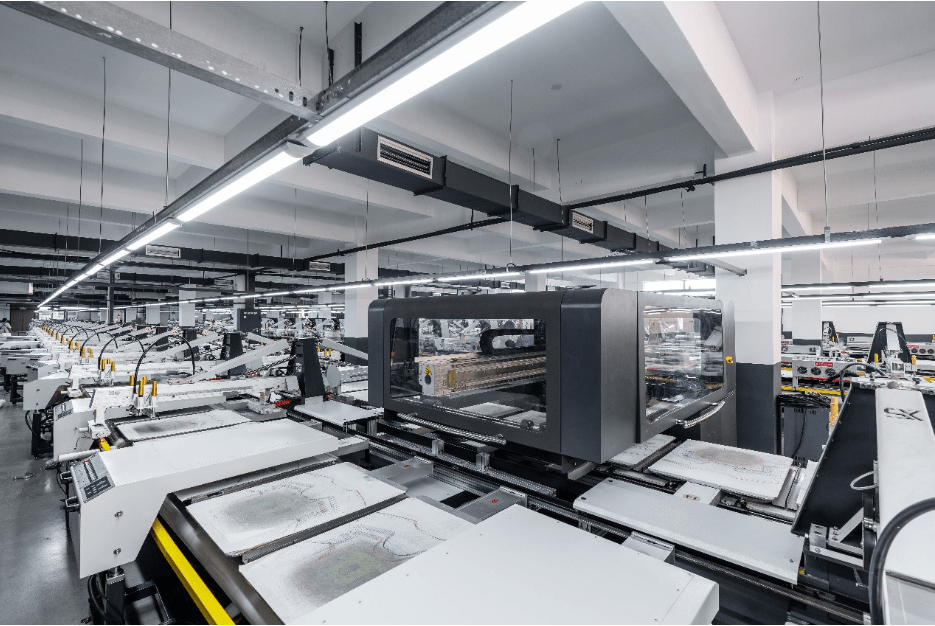

How Digital Printing Works — Example: Hanin DA066M Hybrid Digital Textile Printer
Using the DA066M as an example, a typical digital garment workflow includes three key stages:
1. Surface Pre-Treatment
Before printing, the garment (e.g., 100% cotton) is pre-treated with a dedicated coating to enhance ink adhesion and reduce bleeding. The DA066M line supports manual or automated pre-treatment/drying modules to ensure even coverage and stable results. After pre-treatment, dry the garment via heat press or IR/hot-air to reach a print-ready state.
Tips: control add-on and uniformity; dry to a clean, matte surface; validate settings per fabric/ink with small tests.
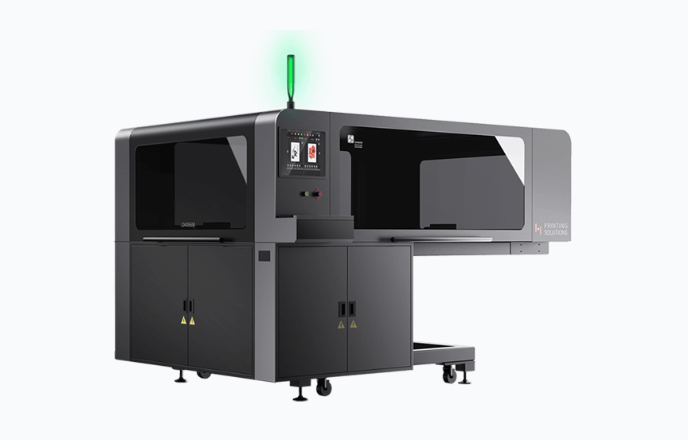

2. Digital Printing Process
With the fabric prepared, the DA066M reads design files (e.g., PNG/TIFF/PDF) via supported RIPs (e.g., Hanin Task Service, Hanin RIP, NeoStampa). Industrial inkjet heads jet micro-droplets directly onto the textile for sharp edges and smooth tonal transitions.
• White ink & dark fabrics: choose DA066M configurations with white channels for digital white underbase, or pair the line with a screen-printed white base to boost opacity and speed.
• Print area & stations: typical max print area up to 600 × 900 mm (customizable). The oval, multi-station architecture allows flexible pairing with screen, drying, QC, and other units to raise overall takt time and accelerate style changeovers.
• Parameter tuning: set resolution, pass count, and carriage speed according to artwork detail and throughput targets; confirm via sample prints and wash/rub tests.
3. Heat Curing and Fixation
After printing, the garment enters the curing stage. A heat press or conveyor dryer is used to thermally fix the pigments to the fabric fibers, following a temperature–time profile that matches the specific ink system and fabric type. This process ensures strong bonding, excellent wash fastness, and a smooth, comfortable hand feel.
• Parameter Range: Curing conditions vary depending on the ink brand, formulation, and fabric characteristics. It is recommended to follow the Technical Data Sheet (TDS) provided by the ink or process supplier and to verify the optimal curve through small-scale test runs.
• Quality Control Tips: Conduct routine checks for domestic and commercial wash fastness, dry and wet rub fastness, appearance, and dimensional stability. Adjust pre-treatment and curing parameters as needed to maintain consistent color and durability.
Key Differences: Screen Printing vs Digital Printing
| Criteria | Screen Printing | Digital Printing | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Process | Requires one screen per color; time-consuming prep | No screens; prints directly from file | Digital eliminates setup—ideal for small runs |
| Production Speed & Quantity | Very fast for large, uniform batches | Faster for short runs and frequent changes | Screen = volume speed; Digital = changeover speed |
| Color Range & Detail | Limited by number of screens; flatter tones | CMYK (+ extended gamut), gradients, photo detail | Digital wins for complex, multicolor designs |
| Cost Efficiency | Low per-unit at scale; high setup | Low startup; variable per-unit | Digital is cheaper for small/medium orders |
| Durability & Feel | Thicker ink layer; extremely durable | Softer hand; durability depends on ink/curing | Modern pigment workflows achieve Grade 4–5 wash fastness |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water/chemical use | Minimal wastewater; water-based inks | Digital is cleaner and more sustainable |
1. Setup Process – Flexibility Starts Here
Screens require coating, exposure, and drying. Digital bypasses this—load file, print. Lead time and labor drop dramatically, enabling true on-demand production.
2. Production Speed & Quantity – Different Kinds of Efficiency
Screen excels at thousands of identical items once set up. Digital shines for short runs, frequent style changes, or variable data since there’s no downtime for color/artwork swaps. Rule of thumb: Screen for volume; digital for agility.

3. Color Range & Detail – Precision Beyond Limits
Screen applies spot colors in layers (great for solids, weaker for gradients/photos). Digital jets CMYK (and extended gamut) for gradients, shadows, and photo-realism—perfect for detailed or gradient-rich artwork.
4. Cost Efficiency – The Real Break-Even
Screen’s unit cost drops with scale but setup is expensive. Digital’s startup cost is near zero, so it’s ideal for short to mid-size batches. In many scenarios, the break-even falls around 300–500 pieces, depending on labor rates and color count.
5. Durability & Feel – Thickness vs Softness
Screen yields a thicker, tactile layer with excellent durability. Digital (pigment/reactive workflows) achieves Grade 4–5 wash fastness with a softer, lighter hand. Both can be long-lasting; digital typically feels smoother on-body.
6. Environmental Impact – Sustainability Wins
Screen uses more water and chemicals for emulsions and cleanup. Digital uses water-based inks and generates minimal wastewater, supporting sustainability and regulatory compliance.
When to Use Screen Printing vs Digital Printing
| Use Case | Best Method | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk T-shirts (1,000+ pcs) | Screen Printing | Lower unit cost at scale |
| Small fashion collections | Digital Printing | Quick changeovers, no screens |
| Photo or gradient designs | Digital Printing | Superior detail and color blending |
| Cotton garments | Both | Depends on design and volume |
| Synthetic or blended fabrics | Digital Printing | Compatible with multiple ink types |
| Eco-conscious brands | Digital Printing | Low waste and water usage |
| Special effects (metallic, puff, glitter) | Screen Printing | More durable/versatile for textured effects |

For businesses upgrading from traditional to digital workflows, the Hanin DA066M offers a seamless transition—combining a high-capacity oval platform with digital flexibility, industrial-grade printheads, smart control, and eco-friendly water-based inks.
Screen Printing vs Digital Printing — Common Questions
1. Can digital printing replace screen printing?
In most apparel and home-textile applications, digital printing can meet nearly all design requirements. However, for special visual effects (such as metallic, puff, or glitter inks) or ultra-large, cost-sensitive mass production, screen printing still holds an advantage.
2. Who is the DA066M best suited for?
The Hanin DA066M is ideal for brands and factories requiring high productivity with frequent design changes. Its “screen + digital” hybrid configuration offers unmatched flexibility for adaptive production lines that combine the strengths of both technologies.
3. Can it print on dark fabrics?
Yes. The DA066M W model includes white ink channels, or users can integrate a screen-printed white base into the workflow to achieve full-color printing on dark garments.
4. Is pre-treatment and specific curing required?
Yes, depending on the fabric type and ink chemistry. Always follow the official technical guidelines and the recommendations of ink/process suppliers to ensure optimal colorfastness and hand feel.
5. How environmentally friendly is it?
The DA066M’s plate-free digital workflow significantly reduces chemical usage and water consumption compared with traditional screen printing. Its sustainability performance aligns with modern eco-compliance and green manufacturing goals, though exact water-saving levels depend on the specific process setup and production line configuration.
Screen printing remains valuable for very large, uniform jobs. But the future of textile production is digital—faster setup, virtually unlimited color, and dramatically lower environmental impact.
As an industrial digital textile printer manufacturer, Hanin empowers global partners with end-to-end digital solutions—from prototype to mass production.
Ready to modernize your print operation?
Engineered for precision, speed, and sustainability.